In the rapidly evolving world of cryptocurrencies, alt coins have emerged as a vibrant and diverse category that extends beyond the realm of Bitcoin. These alternative coins, often referred to as "alt coins," represent a dynamic spectrum of digital currencies that have gained prominence alongside Bitcoin's ascent.
As technological innovation continues to drive the blockchain space forward, alt coins have captivated the attention of investors, traders, and enthusiasts, offering a plethora of features, use cases, and potentials.
This blog delves into the realm of alt coins, unveiling their distinct characteristics, historical significance, and differentiated purposes compared to Bitcoin. From their inception as a response to Bitcoin's limitations to the present-day landscape of innovation and competition, we'll journey through the nuances of alt coins. Moreover, we'll dive into notable alt coins that have captured the spotlight, shedding light on their essential aspects, functionalities, and the impact they've made on the cryptocurrency landscape.
Whether you're an investor seeking diversified opportunities or a curious observer navigating the complexities of cryptocurrencies, this blog serves as a comprehensive guide to learning about the world beyond Bitcoin: the alt coins!
Some of the concepts covered in this blog are taken from this Quantra course on Crypto Trading Strategies: Intermediate. You can take a Free Preview of the course by clicking on the green-coloured Free Preview button.
This blog covers:
- What are alt coins?
- History of alt coins
- Purpose and differentiation of alt coins from bitcoin
- Popular alt coins
- How to trade alt coins?
- Regulations and laws
- Myths debunked
- Challenges of alt coins and ways to overcome them
- Future of alt coins
What are alt coins?
Alt coins, short for "alternative coins," are any cryptocurrency other than Bitcoin (BTC). These coins have emerged as alternatives to Bitcoin and offer a wide range of features, use cases, and technologies beyond what Bitcoin offers. alt coins have contributed to the diversification of the cryptocurrency landscape and have sparked innovation in various areas of blockchain technology and finance.
Definition of alt coins
Alt coins encompass a diverse set of cryptocurrencies that were created after the success of Bitcoin. These coins aim to address limitations, introduce new features, or cater to specific niches within the cryptocurrency ecosystem.
History of alt coins
The concept of alt coins originated soon after Bitcoin's introduction in 2009. The first alt coin, "Namecoin," was launched in 2011 and aimed to provide decentralised domain name registration. This marked the beginning of a wave of alternative cryptocurrencies. Some alt coins aimed to address perceived shortcomings in Bitcoin's design, such as transaction speed, scalability, or privacy features.
Purpose and Differentiation of alt coins from bitcoin
Alt coins serve various purposes, which can include:
- Improved Features: alt coins often introduce technological enhancements not found in Bitcoin. For instance, Litecoin (LTC) was designed to provide faster transaction confirmation times compared to Bitcoin's blockchain.
- Privacy and Anonymity: Cryptocurrencies like Monero (XMR) and Zcash (ZEC) emphasise enhanced privacy features, allowing users to conduct transactions with greater anonymity.
- Smart Contracts and DApps: Ethereum (ETH) introduced the concept of smart contracts, enabling the creation of decentralised applications beyond simple transactions.
- Niche Markets: Some alt coins target specific industries, such as supply chain management (VeChain), digital content ownership (Basic Attention Token), or Internet of Things (IOTA).
- Governance and Consensus: Dash (DASH) incorporates a decentralised governance system, allowing holders to influence the coin's development, while Cardano (ADA) emphasises academic research and formal verification.
- Stablecoins: alt coins like Tether (USDT) and USD Coin (USDC) are pegged to stable assets like fiat currencies, providing stability for traders and users.
It's important to note that while alt coins offer unique features and benefits, they also come with their own set of risks and challenges. Their success can be influenced by factors such as adoption of new technologies, technological advancements, regulatory environment, and market sentiment.
In summary, alt coins represent a diverse collection of cryptocurrencies that have emerged as alternatives to Bitcoin, each with its own purpose, features, and use cases. They contribute to the dynamic evolution of the cryptocurrency ecosystem and have fostered innovation in blockchain technology and beyond.
Popular alt coins
In 2023, the following three have been declared as the most popular alt coins:
Caged Beasts
Introduction to Caged Beasts
"Caged Beasts" is a novel cryptocurrency project currently in its presale phase. With a captivating backstory centred around Dr. Jekyll and a mysterious creature named Rabbit Hyde, it's gaining attention in the crypto community. While it's still in its early stages, Caged Beasts has ambitious plans outlined in its roadmap. It's worth keeping an eye on for meme coin enthusiasts and those interested in unique crypto narratives.
How does Caged Beasts work?
Caged Beasts aims to create an engaging and thrilling crypto environment that goes beyond traditional cryptocurrencies. It values community involvement and offers exclusive benefits, including access to prized NFTs, to its members.
Let us see an overview of how Caged Beasts work below:
- Community Focus: Caged Beasts stands apart from traditional cryptocurrencies with its unique focus on building a vibrant community. The project aims to create an ecosystem that thrives on excitement and active participation.
- Exciting Competitions: Caged Beasts plans to offer thrilling competitions that engage and captivate investors. These competitions are designed to add an element of adventure and fun to the crypto experience.
- Generous Bonuses: Investors can look forward to mind-boggling bonuses as part of their engagement with Caged Beasts. These bonuses are likely to be enticing incentives for community members.
- Captivating Events: The project promises an array of captivating events that will keep the community engaged and excited. These events could range from virtual gatherings to interactive activities.
- Community Empowerment: Active participation within the Caged Beasts community holds significant importance. Members are encouraged to shape the project's ecosystem and contribute to its growth.
- Exclusive NFT Access: Being part of the Caged Beasts community comes with perks. Members can enjoy exclusive VIP access to highly sought-after NFT releases. This allows them to collect and own coveted NFTs that are sure to impress.
Shiba Inu
Introduction to Shiba Inu
Introduction: Shiba Inu (SHIB) is a cryptocurrency token inspired by the popular "Doge" meme featuring the Shiba Inu dog breed. It gained widespread attention as a meme coin in the world of cryptocurrencies. Shiba Inu aims to create a decentralised ecosystem with a focus on community and fun.
How does Shiba Inu work?
Shiba Inu (SHIB) is a playful and community-driven cryptocurrency, inspired by the Dogecoin meme. It encourages a vibrant community with initiatives like ShibaSwap and NFT collaborations. Its unique tokenomics and meme culture have garnered attention, making it a distinctive player in the crypto world, known for its fun-loving approach.
Let us see an overview of how Shiba Inu works below:
- Community-Driven: Shiba Inu is a community-driven project, meaning its development and direction are influenced by its community of users and supporters.
- Tokenomics: SHIB is an ERC-20 token on the Ethereum blockchain. It has a large total supply, which encourages widespread distribution. Holders of SHIB can participate in various aspects of the Shiba Inu ecosystem.
- ShibaSwap: Shiba Inu introduced ShibaSwap, a decentralised exchange and yield farming platform. Users can stake their SHIB tokens to earn rewards and liquidity providers can earn fees.
- NFTs and Art: Shiba Inu has also ventured into the world of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and digital art, collaborating with artists to create unique NFT collections.
- Burn and Vitalik Buterin's Role: Part of the SHIB token supply was sent to Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin's wallet, and he subsequently burned a significant portion of it. This action aimed to reduce the token's supply and add value.
- ShibaSwap and Bone Token: Shiba Inu introduced a governance token called "Bone" in connection with ShibaSwap, allowing users to participate in decision-making for the platform.
Uniswap
Introduction to Uniswap
Uniswap is a decentralised cryptocurrency exchange (DEX) built on the Ethereum blockchain. It's designed to enable users to swap various Ethereum-based tokens without the need for a traditional intermediary, such as a centralised exchange. Uniswap is a significant player in the decentralised finance (DeFi) ecosystem.
How does Uniswap work?
Uniswap, a decentralised exchange on the Ethereum blockchain, empowers users to swap cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. It relies on liquidity pools provided by users and is governed by UNI token holders who make key decisions about the platform's future. This open and community-driven approach has made Uniswap a cornerstone of decentralised finance (DeFi).
Let us see an overview of how Uniswap works below:
- Automated Liquidity: Uniswap operates on the principle of automated liquidity provision. Users can add liquidity to pools by depositing pairs of tokens. These liquidity pools facilitate token swaps.
- Constant Product Formula: Uniswap uses a mathematical formula called the "constant product formula" to determine the exchange rate between two tokens in a liquidity pool. As one token is swapped for another, the formula ensures that the product of the quantities of the two tokens remains constant.
- Token Swaps: Users can easily swap one token for another by accessing the Uniswap interface. Uniswap automatically calculates the exchange rate and fees based on the liquidity pool's contents.
- Liquidity Providers: Liquidity providers earn fees for supplying tokens to the pools. They receive a portion of the trading fees generated by users who swap tokens in the pool.
- UNI Token: Uniswap has its governance token called "UNI." UNI holders can participate in the decision-making process for the platform, including proposing and voting on changes and upgrades.
- Liquidity and Accessibility: Uniswap has played a pivotal role in making decentralised finance accessible and has become a cornerstone of the DeFi ecosystem, allowing users to access a wide range of tokens and create new markets.
Other most popular alt coins
Some of the other most popular alt coins are:

Let us see each of the most popular alt coins in detail below:
Ethereum
Introduction to Ethereum
Ethereum is a decentralised blockchain platform that has gained immense popularity for its ability to support the development of smart contracts and decentralised applications (DApps). It was proposed by a programmer named Vitalik Buterin in late 2013, and its development was crowdfunded in 2014 through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO). Ethereum's mainnet was launched on July 30, 2015.
How does Ethereum work?
Ethereum functions as a decentralised virtual machine that enables developers to create and deploy smart contracts and DApps without the need for intermediaries.
Here's a brief overview of how Ethereum works:
- Decentralised Network: Ethereum operates on a global network of nodes (computers) that run the Ethereum software. These nodes work together to validate and record transactions on the blockchain.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute actions when predefined conditions are met. This allows for trustless and automated interactions.
- Ether (ETH): Ether is Ethereum's native cryptocurrency, often referred to as "fuel" for the network. It is used to pay for transaction fees, execute smart contracts, and participate in various activities within the Ethereum ecosystem.
- Gas Fees: To prevent misuse and prioritise transactions, Ethereum employs a concept called "gas." Gas represents the computational effort required to process transactions and smart contracts. Users pay gas fees in ETH to incentivize miners to include their transactions in the blockchain.
- Decentralised Applications (DApps): DApps are applications that run on the Ethereum blockchain. They can be anything from financial platforms to games and decentralised social networks. Ethereum provides a platform for developers to create and deploy these applications.
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): The EVM is a runtime environment that executes smart contracts. It ensures that computations are consistent across all nodes, regardless of their operating system or hardware.
- Upgrades and Improvements: Ethereum has undergone various upgrades to improve its scalability, security, and functionality. Notable upgrades include Ethereum 2.0, which aims to transition from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism to enhance scalability and sustainability.
Ethereum's impact on the blockchain space has been substantial, and it continues to evolve with ongoing upgrades and improvements.
Binance Coin (BNB)
Introduction to Binance Coin (BNB)
Binance Coin (BNB) is the native cryptocurrency of the Binance exchange, one of the largest and most well-known cryptocurrency exchanges in the world. BNB was initially created as a utility token to be used within the Finance ecosystem to provide various benefits to traders and users of the platform. Over time, B&Bs use cases have expanded beyond just being a utility token for the exchange.
How does Binance Coin Work?
Binance Coin operates on the Binance Chain, a blockchain created by Finance specifically for the issuance and management of tokens.
Here's an overview of how BNB works:
- Utility Token: BNB was initially introduced as a utility token on the Binance platform. Users could use BNB to pay for trading fees on the exchange, receiving discounts in the process. This incentivized traders to hold and use BNB, contributing to its popularity.
- Token Launchpad: Binance introduced a token launch platform called Binance Launchpad. Projects could raise funds by conducting token sales using BNB. This attracted attention and increased demand for BNB.
- Binance Smart Chain (BSC): Binance later introduced the Binance Smart Chain, a parallel blockchain that runs alongside the Binance Chain. BSC aims to provide fast and low-cost transactions and supports smart contracts, competing with Ethereum's capabilities.
- DeFi and DApps: BSC's compatibility with Ethereum's tooling has led to the creation of various DeFi applications and decentralised applications (DApps) on the Balance Smart Chain. This expanded BNB's use cases to include participation in the broader DeFi ecosystem.
- Cross-Chain Bridge: Binance has also introduced a cross-chain bridge that enables the movement of assets between Binance Chain, Binance Smart Chain, and other blockchains. This increases interoperability and accessibility.
- NFTs and Gaming: B&Bs popularity has led to its use in the creation and trading of non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and in various gaming-related applications. For example, CryptoQuest is an online blockchain-based role-playing game where players can explore virtual worlds, battle monsters, and collect unique in-game items as NFTs.
Cardano (ADA)
Introduction to Cardano (ADA)
Cardano is a decentralised blockchain platform that aims to provide a more secure and scalable infrastructure for the development of smart contracts and decentralised applications (DApps). Founded by Ethereum co-founder Charles Hoskinson, Cardano stands out for its research-driven approach and commitment to addressing scalability, sustainability, and interoperability challenges within the blockchain space.
How does Cardano Work?
Cardano employs a multi-layer architecture that separates the platform into different components, each with its own specific role.
Here's an overview of how Cardano works:
- Settlement Layer (CSL): The first layer, known as the CSL, focuses on handling ADA transactions. ADA transactions are nothing but a digital currency. CSL ensures secure and efficient transfer of ADA, Cardano's native cryptocurrency.
- Computation Layer (CCL): The second layer, the CCL, is responsible for executing smart contracts and DApps. This separation allows for increased flexibility and upgradeability without affecting the core settlement layer.
- Ouroboros Proof-of-Stake Consensus: Cardano uses the Ouroboros consensus mechanism, a proof-of-stake (PoS) protocol designed to be energy-efficient and secure. It relies on a stakeholder-based approach to validate transactions and create new blocks.
- Research-Backed Approach: Cardano emphasises academic research and peer-reviewed development. This approach aims to provide robust solutions by integrating formal methods and academic rigour into the design and development process.
- Layered Approach: Cardano's layered architecture allows for modular updates and improvements to individual components without disrupting the entire platform. This enhances Cardano's adaptability and scalability.
Cardano's development is ongoing, and its unique approach to scalability, sustainability, and research-driven development has garnered significant attention within the blockchain community.
Solana (SOL)
Introduction to Solana (SOL)
Solana is a high-performance blockchain platform designed for decentralised applications (DApps) and crypto-currencies. It aims to provide fast transaction speeds, high throughput, and low fees, making it suitable for real-time applications and decentralised finance (DeFi) projects. Solana was founded by Anatoly Yakovenko in 2020 and has gained attention for its innovative approach to solving scalability challenges.
How does Solana Work?
Solana's architecture is built around a unique combination of technologies that work together to achieve its high performance.
Here's an overview of how Solana works:
- Proof-of-History (PoH): Solana employs a concept called Proof-of-History, which creates a historical record of events on the blockchain. PoH establishes a sequence of timestamps, allowing validators to reach consensus more efficiently and reducing the time required for confirmations.
- Tower BFT Consensus: Solana uses a consensus mechanism called Tower BFT. This consensus mechanism enhances security and enables faster finality for transactions.
- Gulf Stream: Solana introduces a mechanism called Gulf Stream, which helps nodes discover the current state of the network more rapidly. This reduces latency and enables faster communication among nodes.
- Sealevel Runtime: Solana's Sealevel runtime provides a high-performance execution environment for smart contracts. It is designed to optimise transaction processing and provide efficient support for DeFi applications.
- Parallel Processing: Solana uses parallel processing to execute transactions concurrently, further increasing the platform's throughput and reducing latency.
Solana's approach to solving scalability and performance challenges has positioned it as a prominent player in the blockchain space.
Ripple (XRP)
Introduction to Ripple (XRP)
Ripple is a technology company that has developed a blockchain-based platform and digital currency designed to facilitate fast and cost-effective cross-border payments and remittances. Founded in 2012, Ripple aims to solve the inefficiencies and delays associated with traditional international payment systems by providing a real-time, on-demand settlement network.
How does Ripple Work?
Ripple's technology is centred around its native cryptocurrency, XRP, and its underlying blockchain network.
Here's an overview of how Ripple works:
- Consensus Algorithm: Ripple uses a unique consensus algorithm called the Ripple Protocol Consensus Algorithm (RPCA). Unlike traditional proof-of-work (PoW) or proof-of-stake (PoS) mechanisms, RPCA doesn't require mining or extensive computational power. Instead, a group of trusted validators agrees on the state of the ledger.
- Ledger and XRP: Ripple has a distributed ledger that records all transactions on the network. XRP, the native cryptocurrency, is used as a bridge currency to facilitate transfers between different currencies. This allows for quicker and more cost-effective cross-border transactions.
- RippleNet: Ripple's network, known as RippleNet, consists of financial institutions, banks, and payment providers that use Ripple's technology to settle cross-border transactions. RippleNet includes various products and services, such as xCurrent (for messaging and settlement) and On-Demand Liquidity (ODL) (for using XRP as a bridge currency).
- Real-Time Settlement: Ripple's focus on real-time settlement means that transactions can be completed within seconds, as opposed to the multi-day settlement times often associated with traditional systems.
Ripple's technology has had a significant impact on the financial industry's approach to cross-border payments.
How to trade alt coins?
Trading alt coins involves buying and selling alternative cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin (BTC). It's important to note that alt coin trading is highly speculative and comes with risks, including market volatility and potential losses.
Here's a general guide on how to trade alt coins:
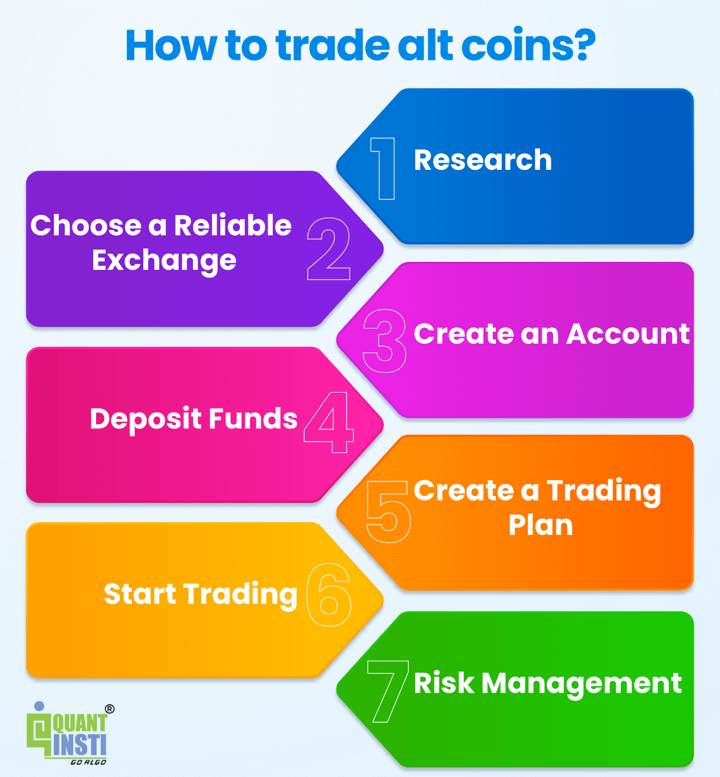
Step 1 - Research
Start by researching and understanding the alt coins you're interested in. Look into their technology, use cases, team, market trends, and community sentiment. Make sure you have a good grasp of the alt coin's potential before trading.
Step 2 - Choose a Reliable Exchange
Select a reputable cryptocurrency exchange where you can trade alt coins. Some popular exchanges for alt coin trading include Binance, Coinbase Pro, Kraken, and Huobi. Ensure the exchange offers a variety of alt coins and has strong security measures.
Step 3 - Create an Account
Sign up for an account on the chosen exchange. This usually involves providing your email, creating a password, and verifying your identity.
Step 4 - Deposit Funds
Deposit funds into your exchange account. This is typically done through bank transfers, credit/debit cards, or other payment methods accepted by the exchange.
Step 5 - Create a Trading Plan
Develop a trading plan that outlines your goals, risk tolerance, entry and exit strategies, and the amount of capital you're willing to invest. Stick to your plan and avoid making impulsive decisions.
Step 6 - Start Trading
Once you're comfortable with your research and have a plan in place, you can start trading. Place buy and sell orders based on your analysis and trading strategy.
Step 7 - Risk Management
Use risk management techniques to protect your investment. This might involve setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and not investing more than you can afford to lose.
Regulations and laws
The regulatory landscape for alt coins, like all cryptocurrencies, varies significantly from one jurisdiction to another. Regulations are influenced by factors such as the nature of the alt coin, its use cases, the country's stance on cryptocurrencies, and the existing legal and financial frameworks.
Here are some key aspects of the regulatory landscape for alt coins:

1. Securities Regulation: Some alt coins may be considered securities by regulatory authorities, especially if they are issued through initial coin offerings (ICOs) or token sales. Securities regulations are designed to protect investors and ensure transparency. alt coins that are classified as securities may be subject to registration, disclosure requirements, and compliance with securities laws.
2. AML/KYC Compliance: Regulators often require cryptocurrency exchanges and platforms to implement anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) procedures. This helps prevent illegal activities like money laundering and terrorist financing and ensures that users' identities are verified.
3. Consumer Protection: Regulators may impose rules to protect consumers who invest in or use alt coins. This can involve enforcing transparency in marketing, ensuring accurate information is provided to users, and addressing potential risks associated with alt coin investments.
4. Payment Services and Money Transmission: Depending on their use cases, certain alt coins could fall under regulations related to payment services and money transmission. Licensing and compliance requirements may be necessary for entities facilitating alt coin transactions.
5. Securities Offerings: If an alt coin is marketed or sold to the public as an investment opportunity with the expectation of profits, it could be classified as a security. In such cases, regulatory bodies may require the issuer to register the offering or comply with exemptions.
6. Taxation: Tax treatment of alt coins can vary widely. Some jurisdictions treat alt coin transactions similarly to traditional currency transactions, while others classify them as something that is subject to capital gains tax. Clear guidance on alt coin taxation is crucial for users and businesses.
7. Regulatory Sandboxes: Innovative projects in the alt coin space may be allowed to operate within regulatory sandboxes in some countries. Sandboxes provide a controlled environment where startups can test new products and services under the supervision of regulatory authorities.
8. Alignment of frameworks at an international level: As cryptocurrencies operate across borders, international coordination is becoming more important. Regulatory bodies are working to develop common approaches to issues like AML compliance, but there are still challenges due to differing national regulations.
The regulatory landscape for alt coins is still evolving, and regulations may change over time as governments and authorities adapt to the rapidly changing cryptocurrency ecosystem.
Given the complexity of regulatory environments, alt coin projects and users should stay informed about the legal requirements and obligations in their respective jurisdictions. Consulting legal professionals with expertise in cryptocurrency regulations can provide guidance on compliance and risk mitigation.
Disclaimer: We do not endorse or encourage the trading of any financial instrument in any market. Engaging in trading activities is solely at the discretion and responsibility of the individual trader. It is essential for traders to conduct their own research, assess risks, and make informed decisions. The information provided should not be considered as financial advice.
Myths debunked
Here's a table outlining some common myths and false claims about alt coins:
|
Myth / False Claim |
Reality |
|
Alt coins are all the same as Bitcoin |
Alt coins have distinct features, technologies, and use cases, differentiating them from Bitcoin. |
|
Alt coins will replace Bitcoin |
Bitcoin remains the flagship cryptocurrency and holds a dominant position in the market. Alt coins complement the crypto ecosystem. |
|
Alt coins have no purpose |
Alt coins serve various purposes, from decentralised applications to enhancing privacy and scalability. Many alt coins facilitate real-world applications, including DeFi, NFTs, supply chain, and more. |
|
Alt coins may make you instantly reap good returns |
Success in alt coin trading requires research, a well performing strategy, and risk management measures, just like any investment. Although, even after this, your success may not be assured. |
|
Alt coins are all technologically superior to Bitcoin |
While some alt coins introduce innovations, not all are necessarily more technologically advanced than Bitcoin. |
Challenges of alt coins and ways to overcome them
Let us now find out some of the challenges and the ways to overcome them while trading alt coins.
|
Challenges |
Ways to Overcome |
|
1. Volatility |
Risk Management: Set stop-loss and take-profit orders to limit potential losses. Diversification: Spread your investments across different alt coins to reduce exposure to a single asset. Stay Informed: Monitor market news and trends that could impact prices. |
|
2. Lack of Regulation |
Research Jurisdictions: Understand the regulatory environment in your country and the alt coins you're interested in. Choose Reputable Exchanges: Use well-regulated exchanges that comply with local regulations. |
|
3. Security Concerns |
Use Hardware Wallets: Store your alt coins in hardware wallets to avoid hacks. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of security to your exchange accounts. Regularly Update Software: Keep your wallets and software up to date to benefit from security patches. |
|
4. Limited Information |
In-Depth Research: Dig deep into whitepapers, project websites, team backgrounds, and community discussions. Join Communities: Engage with alt coin communities on social media and forums to gather insights. |
|
5. Pump and Dump Schemes |
Avoid FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): Be cautious of sudden price spikes and do your research before investing. Find out the reason behind such spikes and only trade if these reasons are valid. Verify Information: Verify the authenticity of news or announcements before acting on them. Long-Term Approach: Focus on projects with solid fundamentals rather than short-term pumps. |
|
6. Unpredictable Market Sentiment |
Stay Updated: Follow cryptocurrency news outlets and social media for the latest information and take an Analytical Approach. |
Remember that trading alt coins involves risks, and it's essential to conduct thorough research, practise responsible risk management, and only invest what you can afford to lose. Every trader's situation is unique, so tailor your approach based on your knowledge, experience, and risk tolerance.
Future of alt coins
The future of alt coins, like any aspect of the cryptocurrency and blockchain space, is subject to speculation and uncertainty.
Current scenario
In September 2023, it is mentioned by an analyst that alt coins could defy expectations and rally ahead of the Bitcoin (BTC) halving.
Bitcoin halving, also known as the "halvening," is an event that occurs approximately every four years in the Bitcoin network. During a halving event, the rewards that miners receive for validating transactions and securing the network are cut in half.
This reduction in rewards has the effect of slowing down the rate at which new Bitcoins are created. Bitcoin halvings are programmed into the cryptocurrency's code and are designed to occur every 210,000 blocks, or roughly every four years. The purpose of halvings is to control inflation and ensure a finite supply of Bitcoin, ultimately leading to a cap of 21 million Bitcoins.
What does this mean for the future of alt coins?
So, when an analyst suggests that alt coins could "rally ahead of the Bitcoin halving," they are speculating that the prices of alternative cryptocurrencies (alt coins) may increase significantly in the months leading up to the next scheduled Bitcoin halving event.
This speculation is based on the idea that as the Bitcoin halving approaches, investors may diversify their cryptocurrency holdings by purchasing alt coins in the hope of achieving higher returns. alt coins could attract attention and investment because they may offer different features or opportunities compared to Bitcoin.
Trends and possibilities to shape future of alt coins
However, there are several trends and possibilities that could shape the future of alt coins:
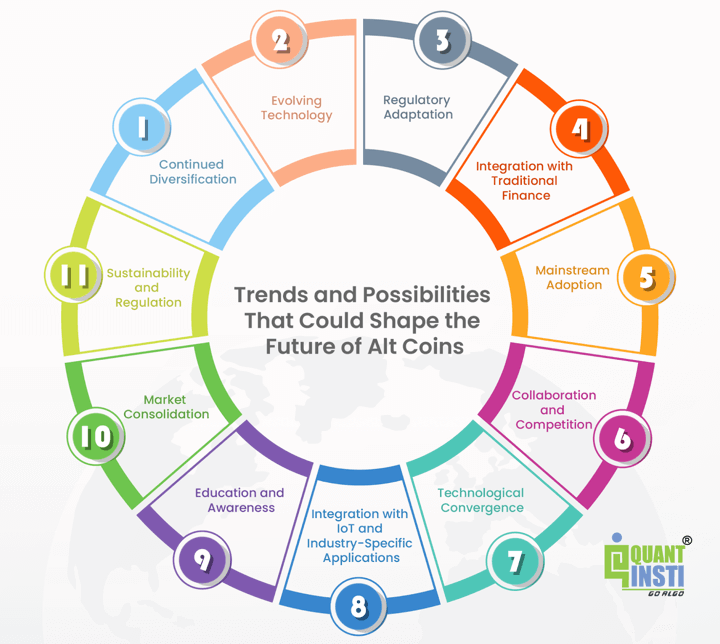
1. Continued Diversification: alt coins will likely continue to diversify, offering a wide range of use cases beyond Bitcoin. This diversification could include innovations in DeFi, NFTs, privacy, scalability, governance, and more.
2. Evolving Technology: alt coins will likely continue to evolve technologically to address current limitations and provide unique features. Improvements in consensus mechanisms, scalability solutions, privacy enhancements, and interoperability could play a significant role.
3. Regulatory Adaptation: As regulatory frameworks around the world continue to develop, alt coins will need to adapt and comply with regulations. Regulatory clarity could positively impact adoption and institutional participation.
4. Integration with Traditional Finance: As the cryptocurrency ecosystem matures, alt coins could see increased integration with traditional financial systems. This could involve partnerships with financial institutions, payment processors, and adoption by governments.
5. Mainstream Adoption: alt coins with compelling use cases and practical applications could see increased adoption by businesses and individuals. Cryptocurrency wallets, payment systems, and decentralised applications (DApps) might become more user-friendly.
6. Collaboration and Competition: alt coins will likely continue to collaborate and compete with each other and with established players in the finance and technology sectors. This competition could lead to more innovation and development.
7. Technological Convergence: As different alt coins develop unique features and solutions, there could be efforts to integrate the best aspects of various projects into a unified system.
8. Integration with IoT and Industry-Specific Applications: alt coins could find applications beyond finance, such as in the Internet of Things (IoT) and specific industries like supply chain management, healthcare, and more.
9. Education and Awareness: As the general public becomes more aware of cryptocurrencies and their potential, alt coins might see increased interest from retail investors and entrepreneurs.
10. Market Consolidation: While many alt coins are innovative and unique, some might not survive in the long term due to competition, lack of adoption, or other factors. This could lead to market consolidation where stronger projects thrive.
11. Sustainability and Regulation: alt coins that address environmental concerns, comply with regulations, and demonstrate long-term sustainability might gain more support and attention.
Conclusion
alt coins have emerged as diverse alternatives to Bitcoin, offering a wide array of features, use cases, and innovations within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. They have contributed to the expansion and diversification of the blockchain space, sparking innovation and driving competition. alt coins address various limitations of Bitcoin while introducing new technologies and concepts.
While alt coins offer exciting opportunities, it's essential to navigate this landscape with caution. Thorough research, responsible risk management, adherence to regulations, and continuous learning are paramount. The future of alt coins is shaped by technological advancements, market trends, and regulatory developments, making it an ever-evolving space worth watching.
As you explore alt coins and consider trading or investing, keep in mind that the cryptocurrency market is speculative and subject to volatility. Stay informed, make informed decisions, and adapt to the dynamic nature of the blockchain ecosystem.
If you wish to dive deeper into the realm of alt coins, we recommend you to explore our course on Crypto Trading Strategies: Intermediate. This is a perfect course for programmers and quants who wish to explore trading opportunities in cryptocurrency. Also, with this course you will learn the risks involved in crypto trading, how to Crypto trade and create 3 different intraday trading strategies in Python.
Disclaimer: All data and information provided in this article are for informational purposes only. QuantInsti® makes no representations as to accuracy, completeness, currentness, suitability, or validity of any information in this article and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. All information is provided on an as-is basis.


