Welcome to our beginner's guide on bullish candlestick patterns - the key to unlocking market trends and making smarter trading decisions.
First things first, we'll walk you through what a candlestick is and how to read candlestick charts.
But do you know how to identify bullish patterns with confidence and validate them with other indicators?
We will learn everything about the bullish candlestick pattern with the real-life example to demonstrate how to use these patterns to set entry and exit points, maximising your profits.
Of course, risk management is crucial. We'll share essential strategies to protect your capital and minimise losses.
By the end of this guide, you'll have all the tools you need to navigate bullish candlestick patterns like a pro. So, let's dive in!
This blog covers:
- What is a candlestick?
- How to read candlestick charts?
- What is the bullish candlestick?
- Common bullish candlestick patterns
- How do you identify a bullish pattern?
- Example with steps for using bullish candlestick pattern in trading
- Risk management with bullish candlestick pattern
- How to validate bullish candlestick patterns with other indicators?
What is a candlestick?
Candlesticks are a crucial element of quantitative trading, serving as visual representations of price movements in financial instruments like securities, derivatives, currencies, and more. They effectively summarise the Open, High, Low, and Close prices over a specific time frame.
Resembling the shape of real-life candlesticks, these charts earned their name. By utilising candlestick charts, traders gain valuable insights into market trends and price action, enabling them to make informed decisions in quantitative trading strategies.

The colour of the candlestick body can vary, typically being green or white for a bullish (upward) movement, indicating that the closing price was higher than the opening price.
Conversely, the body is usually red or black for a bearish (downward) movement, indicating that the closing price was lower than the opening price. This colour convention may vary depending on the charting software or platform being used.
Candlestick charts offer a visual representation of price action, making it easier for traders to interpret market movements and identify potential trading opportunities.
How to read candlestick charts?
Reading candlestick charts involves understanding the visual patterns formed by the individual candlesticks and interpreting the information they convey.
Here are a few considerations while reading candlestick charts:
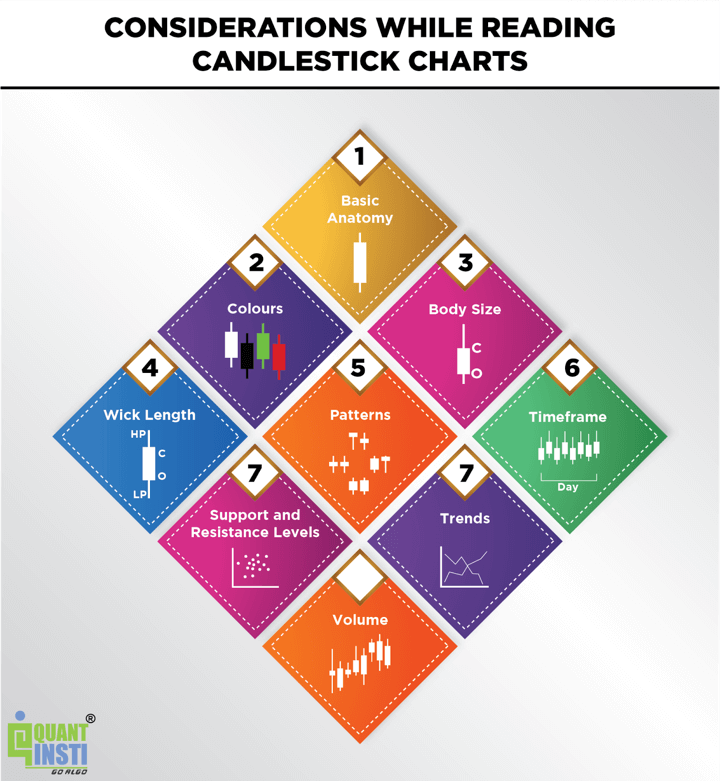
Basic Anatomy
Each candlestick consists of a rectangular body and two thin lines extending from the top and bottom of the body, known as wicks or shadows.
Colours
The colour of the body provides information about the price movement during the specified time interval. A green or white body typically represents a bullish candle, indicating that the closing price was higher than the opening price. A red or black body represents a bearish candle, showing that the closing price was lower than the opening price.
Body Size
The size of the body represents the price range between the opening and closing prices. A larger body indicates more significant price movement, while a smaller body indicates relatively minor price changes.
Wick Length
The length of the wicks reveals the price range between the high and low prices during the time interval. Longer wicks signify greater price volatility, while shorter wicks indicate a relatively stable price range.
Patterns
Analyse the patterns formed by multiple candlesticks to identify potential market trends and reversals. Some common patterns include doji, hammer, engulfing, and harami. Learning these patterns can help you anticipate market movements.
Timeframe
Choose a specific timeframe for the candlesticks (e.g., one minute, one hour, one day) depending on your trading or analysis strategy. Different time frames provide different levels of detail and may reveal distinct patterns.
Support and Resistance Levels
Look for areas where candlesticks cluster, indicating potential support (where buying pressure increases) or resistance (where selling pressure increases) levels.
Trends
Identify the prevailing market trend by examining the overall pattern of consecutive candlesticks. A series of higher highs and higher lows suggest an uptrend, while lower highs and lower lows indicate a downtrend.
Volume
Consider the trading volume alongside the candlestick patterns. High volume during certain candlestick formations may indicate stronger market sentiment.
What is the bullish candlestick?
If the body is white or green then it means that the close was higher than the open making it a bullish candle.
It implies that the bullish price movements led to the prices going up and hence, the closing price turned out to be higher than the opening price.
Different types of bullish candles
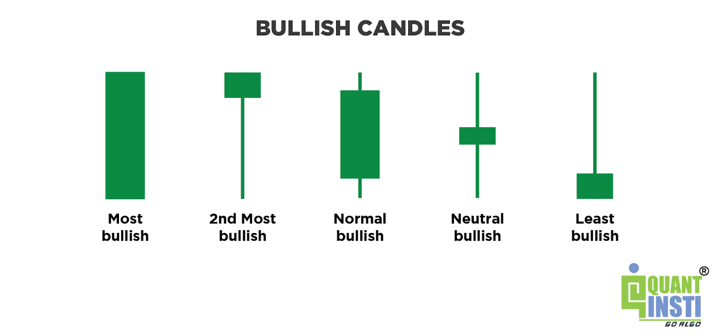
Common bullish candlestick patterns
Bullish candlestick patterns are formations that indicate potential bullish (upward) price reversals or continuation of an existing uptrend. These patterns are often observed during market bottoms or consolidation periods.
Below are some of the common bullish candlestick patterns divided into Single candlestick patterns and Multiple candlestick patterns.
Single Candlestick Patterns:
- Hammer
- Bullish Marubozu
- Dragonfly Doji
- Bullish Belt Hold
Hammer
A hammer candlestick has a small body near the top of the trading range and a long lower wick. It suggests that sellers pushed the price significantly lower during the period, but buyers managed to drive the price back up, indicating potential bullish momentum.
Also, a hammer, when formed in an existing downtrend, is the sign of reversal.

Bullish Marubozu
A bullish marubozu is a candlestick with a long body and little to no wicks. It indicates that buyers have been in control throughout the entire trading period and can signify the continuation of an uptrend.

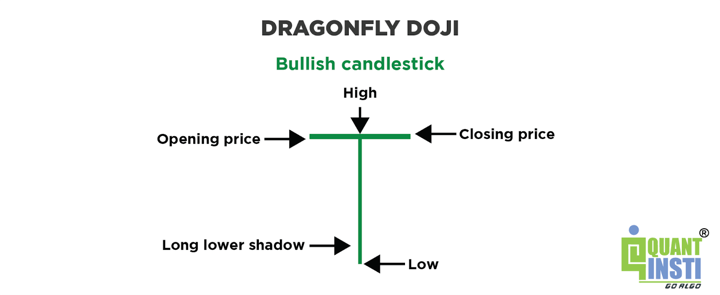
Dragonfly Doji
This is a doji candlestick with a long lower wick and little to no upper wick. It signals that the price opened and closed at the high of the trading period and suggests potential bullish reversal.
Bullish Belt Hold
This pattern consists of a single bullish candlestick that opens near its low and closes near its high, creating a long white body. It is considered a bullish signal, especially if it appears after a downtrend.

Multiple candlestick patterns:
- Bullish Engulfing
- Piercing Line
- Bullish Harami
- Morning Star
Bullish Engulfing
This pattern consists of two candlesticks, where the second (bullish) candlestick's body completely engulfs the first (bearish) candlestick's body. It implies a reversal from a bearish trend to a bullish one, as the buyers overwhelmed the sellers and pushed the price higher.
It is visible in the image below how the bullish candle has completely engulfed the body of previous bearish candlestick.

Piercing Line
The piercing line pattern involves two candlesticks. The first one is a bearish candlestick, followed by a bullish candlestick that opens below the low of the previous candlestick but closes more than halfway into the body of the first candlestick. This pattern suggests a possible trend reversal.
You can see in the image below that the bullish candle has closed above the midline point of the previous bearish candle.

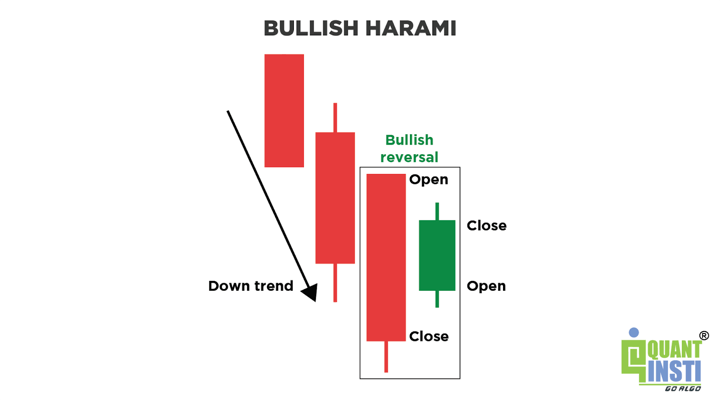
Bullish Harami
This pattern also consists of two candlesticks, where the first one is a large bearish candlestick, followed by a smaller bullish candlestick that is entirely within the range of the first candlestick. It indicates a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
The image below shows a smaller bullish candle as compared to the previous large bearish candle showing downtrend but a reversal is visible.
Morning Star
The morning star pattern is a three-candle pattern. It starts with a large bearish candlestick, followed by a smaller candlestick with a small body (can be bullish or bearish) and a gap with the previous candle. The third candle is a large bullish candlestick that closes beyond the midpoint of the first candle's body. It suggests a strong potential bullish reversal.
You can see in the image below that the second candle closed above 50% of the first candle.

How do you identify a bullish pattern?
Identifying a bullish pattern involves analysing candlestick charts or price charts to spot specific formations that suggest potential upward price movement.
Here's a step-by-step process to identify a bullish pattern:

Step 1: Observe the Chart
First, obtain a candlestick chart or any price chart representing the asset you want to analyse. You can use various charting platforms or financial websites to access these charts.
Step 2: Determine the Trend
Identify the prevailing trend in the price movement. A bullish pattern is more significant if it appears within an existing uptrend, but it can also indicate a potential trend reversal if it occurs during a downtrend.
Step 3: Look for Specific Patterns
Focus on individual candlestick formations or combinations of candlesticks that are indicative of bullish sentiment.
Common bullish patterns include Hammer, Bullish Engulfing, Piercing Line, Bullish Harami, Morning Star, Bullish Marubozu, Dragonfly Doji, and Bullish Belt Hold as already mentioned.
Step 4: Check for Confirmation
Once you identify a potential bullish pattern, look for confirmation from other technical indicators or price patterns. Additional confirmation may come from volume analysis, trendlines, moving averages, or other chart patterns.
Step 5: Consider the Timeframe
Analyse the pattern within a specific timeframe that aligns with your trading strategy. Bullish patterns can appear on various timeframes, such as daily, hourly, or minute charts.
Step 6: Evaluate the Market Context
Assess the broader market context, including fundamental factors and market sentiment, to validate the bullish pattern's significance. Market news and events can influence the reliability of technical patterns.
Step 7: Practise and Experience
Identifying bullish patterns effectively requires practice and experience. Continuously analyse historical charts to improve your pattern recognition skills.
Step 8: Risk Management
Always implement appropriate risk management strategies when trading based on bullish patterns. Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and avoid overcommitting to any single trade.
Example with steps for using bullish candlestick pattern in trading
Using bullish candlestick patterns in trading involves identifying these patterns on the price chart and then using them to make such trading decisions that help maximise the returns.
Here are the steps to use bullish candlestick pattern in trading:
Step 1: Identify the Bullish Candlestick Pattern
We already learnt how to identify the bullish candlestick pattern in the previous section.
Let us move to the next steps.
We can consider identifying the "Hammer" candlestick pattern in our example.

Step 2: Confirm the Pattern
Before making any trading decision, ensure that the pattern is valid and confirmed. Confirming the pattern involves checking the following:
- The current market trend: The "Hammer" pattern is more effective when it appears during a downtrend.
- The candlestick characteristics: In the "Hammer" pattern, the body is small, and there is a long lower wick, resembling a hammer.
Step 3: Entry Point
Once you identify a valid "Hammer" pattern during a downtrend, consider it as a potential entry point for a bullish trade.
Step 4: Stop-loss Placement
Determine an appropriate stop-loss level below the low of the "Hammer" candlestick. This will limit potential losses if the pattern doesn't work as expected.
Step 5: Take-profit Target
Set a target for taking profits, considering previous price resistance levels or other technical indicators.
Summary
- You noticed a "Hammer" candlestick pattern on the daily chart during a downtrend. The stock has been declining for several days, but the "Hammer" pattern suggests a potential bullish reversal.
- The green candlestick with a long lower wick is the "Hammer" pattern. The opening and closing prices are close to each other, near the top of the candlestick, while the long lower wick indicates that prices were pushed lower during the trading session but eventually rebounded.
- Based on the "Hammer" pattern, you decide to enter a long (buy) position on the stock at the opening of the next candle, following the "Hammer" candlestick.
- You place a stop-loss order below the low of the "Hammer" candle to protect against potential losses if the pattern fails.
- As the trade progresses, the stock price starts to rise, and it eventually reaches your predetermined take-profit target. You close the trade, realising a maximised return on investment based on the bullish reversal signalled by the "Hammer" pattern.
Risk management with bullish candlestick pattern
It is a must to remember that no pattern is infallible, and trading always involves risk of losing if the risk is not managed well.
Bullish patterns are best used in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis tools to make well-informed trading decisions.
The best is to regularly update yourself with market trends and market news to enhance your trading acumen.
Let us find out more about risks associated with trading on the basis of bullish candlestick patterns and how to overcome them.
Risk |
Explanation |
Mitigation |
|
False Signals |
Bullish candlestick patterns can lead to losses if the market doesn't confirm. |
Use additional confirmation from indicators or patterns. Look for convergence. |
|
Market Volatility |
High volatility can cause rapid price changes. |
Implement stop-loss orders to limit losses. |
|
Overfitting & Data Mining Bias |
Analysing historical data may produce strategies that don't work in real-time. |
Focus on sound logic, adaptability, and avoid over-reliance on historical performance. |
|
Emotional Trading |
Emotional challenges in following candlestick patterns. |
Develop a disciplined trading plan. Avoid impulsive decisions. |
|
Lack of Proper Money Management |
Trading without a clear money management strategy increases risk. |
Set position sizes based on risk tolerance. Use stop-loss and take-profit orders. |
|
News and Events |
Unforeseen news can quickly change market sentiment. |
Stay updated with news. Consider protective measures during volatile periods. |
|
Market Liquidity |
Illiquid markets may not provide reliable patterns. |
Be cautious in thinly traded assets. Stick to more liquid markets. |
|
Technical Analysis Limitations |
Technical analysis has its limitations. |
Combine with fundamental analysis for a comprehensive view. |
How to validate bullish candlestick patterns with other indicators?
Validating bullish candlestick patterns with other indicators can increase the reliability of your trading signals and reduce the risk of false signals.
Here's how you can do it:
- Trend Confirmation: Before considering a bullish pattern, check the overall trend of the market. A bullish pattern is more reliable when it appears within an existing uptrend. Use trendlines, moving averages, or trend-following indicators like the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) to confirm the trend direction.
- Volume Analysis: Volume can provide valuable insights into the strength of a price movement. Confirm bullish patterns with increasing trading volume, indicating higher buying interest and support for the potential upward move. Use volume indicators like On-Balance Volume (OBV) or Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) to assess volume trends.
- Momentum Oscillators: Oscillators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or the Stochastic Oscillator can help identify overbought or oversold conditions. In the context of bullish patterns, look for oversold readings in the oscillator to support the potential reversal indicated by the candlestick pattern.
- Moving Averages: Compare the price action to different moving averages, such as the 50-day or 200-day moving average. A bullish pattern accompanied by a crossover of short-term moving averages above long-term moving averages may offer additional confirmation.
- Support and Resistance Levels: Identify key support and resistance levels on the price chart. A bullish pattern occurring near a strong support level adds to its significance. Conversely, if the pattern forms near a resistance level, it may signal a potential breakout.
- Fibonacci Retracements: Use Fibonacci retracement levels to identify potential price reversal zones. A bullish pattern coinciding with a retracement level can strengthen the case for a bullish move.
- Multiple Timeframes: Analyse the bullish pattern on multiple timeframes. If the pattern aligns on different timeframes, it provides stronger confirmation. For instance, if you see a bullish pattern on both the daily and weekly charts, it enhances the probability of a successful trade.
Bibliography
- Candlestick pattern
- Candlestick Trading: A Momentum Strategy with Example
- 16 Candlestick patterns
- What is hammer candlestick pattern?
Conclusion
You've now unlocked the power of bullish candlestick patterns. By understanding candlesticks and reading charts, you have the tools to decode market movements with confidence.
Remember, practice and experience are key to identifying bullish patterns effectively. Embrace continuous learning and stay connected with the markets.
With the real-life trading example, you've seen how to apply a bullish pattern strategically for profit. Always prioritise risk management, using stop-loss orders and disciplined plans to protect your capital.
As you embark on your trading journey, keep curiosity alive and explore other indicators to enhance your trading acumen. Best of luck in your trading endeavours, and remember - practice makes perfect! Happy trading!
If you wish to learn more about bullish candlestick patterns, you can enrol into our course on Candlestick Patterns Course based Automated Trading. This course is designed to introduce the learners to patterns formed using candlesticks. Also, the course gives insights on single and multiple candlestick patterns, how to combine them in your trading strategy, and the advantages and disadvantages of trading these candlestick patterns.
Moreover, after completing this course, you can create, backtest, implement, live trade and analyse the performance of candlestick pattern-based trading strategies.
Disclaimer: All data and information provided in this article are for informational purposes only. QuantInsti® makes no representations as to accuracy, completeness, currentness, suitability, or validity of any information in this article and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. All information is provided on an as-is basis.


