By Chainika Thakar, Nitin Thapar & Milind Paradkar
In today’s ever-changing markets, market participants play an extremely imperative role.
Over the past few years, you must have witnessed a sharp positive shift in the financial markets, mainly because of recent rapid advancements in technology. Ever since the advent of technology, trades can be executed at an extremely high pace.
Speaking about technology, mentioning algorithmic trading is a must. With algorithmic trading, the buying and selling (of stocks) occur rapidly every second. Get the edge you need with these comprehensive Algorithmic Trading books.
Edward Leshik and Jane Cralle, the authors of the book, “An Introduction to Algorithmic Trading”, have put down the explanation of getting started with algorithmic trading in the following words,
"In order of complexity, the Markets rank a good 4th after the Cosmos, Human Brain, and Human Immune System.”
Market making is one of the most quantitatively intensive strategies in quantitative trading, it demands real-time data processing, precise pricing models, and automated risk controls working in unison. For traders looking to understand and implement market making strategies, a quantitative trading course that covers execution algorithms and risk management is a strong starting point
In algorithmic trading for beginners, it's crucial to first grasp the fundamentals, such as how algorithms function, the role of Python in executing strategies, and how to analyze market data. Starting with simple trading strategies and gradually progressing to more complex models helps build confidence and develop the skills necessary for success in algorithmic trading.
Coming to the core of this article, let us understand in detail about market making with this blog that covers:
- What is market making and who are market makers?
- How do the market makers earn? How much do market makers make?
- Can market makers lose money?
- Why is market making important?
- Market making and price volatility
- Market making and impact cost
- Algorithmic market making and its benefits
- How automated trading enables market making?
- Difference between a broker and a market maker
- How to become a market maker?
What is market making and who are market makers?
Market making is aimed at infusing liquidity and is mostly a market neutral trading strategy used for securities traded on exchanges. The two most important features of market making are the bid-ask spread and trading volumes. As this process increases the liquidity in the market, it is known as market making.
Mining micro-alphas using trends
Mean-reversion, correlation across assets, and cointegration
Let us learn about market making with an example.
If the market has bid-ask quotes as Rs 50-52 respectively, it means that the market maker will buy at Rs 50 and sell at Rs 52. In this case, if the market maker manages to get a fill for both of his orders at the quoted prices then the profit resulting from this trade would be of Rs 2.
For illiquid securities, the spreads are usually higher, because of the higher risk taken by the market-maker.
Key takeaways about market making from Economic Times ⁽¹⁾:
- Market makers are member firms appointed by the stock exchange to inject liquidity and trade volume into stocks.
- Each market maker displays buy and sell quotations for a guaranteed number of shares.
- Once an order is received from a buyer, the market maker immediately sells from its own holdings or inventory of those shares to complete the order.
- The market maker is compensated for the risk by being allowed to offer two-way quotes in the market, consisting of the buy and sell prices quoted together, the difference being the profit.
- The framework of market makers reduces the time required to execute a trade and the cost of transacting in that stock, allowing a large number of shares to be traded.
Here is a helpful video to learn the fundamentals of market making and how market-makers provide liquidity, manage risks, and contribute to market stability.
How do the market makers earn? How much do market makers make?
Generally, market makers profit by charging higher ask prices (selling) than bid prices (buying). The difference is called the ‘spread’.
The spread compensates the market makers for the risk inherited in such trades which can be the price movement against the market makers’ trading position.
For example, the market maker may purchase 1000 shares of IBM for $100 each (the bid price) and then offer to sell them to a buyer at $100.05 (the ask price).
The difference between the ask and bid price is only $.05, but by trading millions of shares a day, they manage to pocket a significant chunk of profits and can also offset the risk of the price moving against them.

Now, coming to how much the market makers make, according to Glassdoor it is roughly anything between $66,658 to $95,648 per year.
Let us find out ahead in the article if Market Makers end up losing any money or not.
Based on total profit, sharpe ratio, sortino ratio, profit factor, drawdown, and profit per trade
Can market makers lose money?
As mentioned above, the primary risk a market maker can face is a decline in the value of a security after it has been purchased from a seller and before it's sold to a buyer.
Market makers are always counterparties to trades done by informed traders and in case of any volatility in the market; the market makers could get stuck with wrong positions.

Another fatal risk for a market maker is not having the latest information. In simple words, market makers can manage risks and survive only if it is possible for them to receive & respond to information quickly. Or else, the market position could go against them even in a few seconds, which may lead to losses.
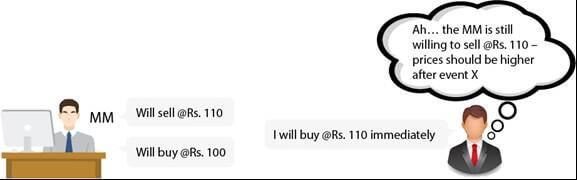
Hence, it is really imperative for strong markets to have strong market makers that survive without incurring huge losses.
Why is market making important?
Generally speaking, market makers help exchanges by maintaining the efficiency of their operations in the markets. This makes market making really important for financial markets. If we take out market makers, there would not be many transactions taking place in the market.
This is the reason that market makers have been an integral part of market infrastructure. Moreover, it is expected that their influence will continue as long as people continue to trade financial assets.
Market making and price volatility
Coming back to the topic of discussion, market makers also help reduce price volatility which leads to fair pricing of the assets.
For example, any given asset has the difference between the best bid and best ask, which is known as the bid-ask spread. Here it is important to note that low liquidity in the markets leads to the wide bid-ask spread. Now, in order to get rid of the wideness in the bid-ask spread, market makers jump in and provide liquidity to the markets.
You can see the image below to understand that the difference between prices of consecutive trades done against a human market maker will be much higher than those done against an automated market maker. And hence, asset price volatility reduces. Also, ahead we will understand how an automated market maker is more efficient than a human counterpart. Learn more about how advanced volatility trading can help enhance your skills.

Before moving ahead watch this concise video to grasp options trading volatility, emphasizing gaining an edge, managing risk, estimating volatility, and practical application.
Market making and impact cost
Since the market makers function with programmatic execution which integrates with exchange APIs, including market making algorithms, it increases their efficiency. And, with that, it leads to better profits since a robust API helps the market makers with reliable up-times and consistent liquidity.
Mining micro-alphas using trends
Mean-reversion, correlation across assets, and cointegration
With automation rendering market making easy, order books have become thick. Execution prices for even big orders are close to a fair price, impact cost & volatility is thus lower.

Algorithmic market making and its benefits
The overall positive impact of algorithmic market making can be summed up as mentioned below:
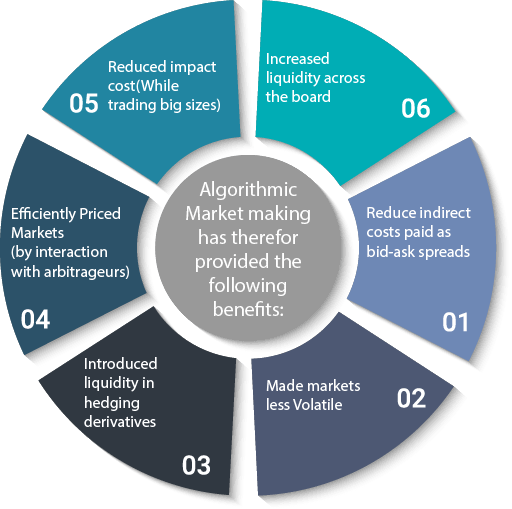
Making markets using algorithms has therefore provided the following benefits:
- Reduced indirect costs paid as bid-ask spreads
- Made markets less volatile
- Introduced liquidity in hedging derivatives
- Efficiently priced markets (by interaction with arbitrageurs)
- Reduced impact cost (while trading big sizes)
- Increased liquidity across the board
How automated trading enables market making?
Since automated systems are more efficient than human beings in detecting & responding to risk-oriented events, it is observed that automated systems help market makers considerably.
Factually, to be efficient, market makers should be able to adjust their quotes immediately in response to market events. But a human being can work only at a particular pace which is comparatively much lesser than the pace of an automated system.
There could be several such events in which the market makers would be needed to react promptly so as to be able to gain out of them.
For instance, these are the two of those events:
- Changes in the prices of financial instruments, and
- Trading positions accumulated by the market maker
Since automated systems can handle their risks much more accurately than humans, they offer better quotes for the Market Makers.
While using automated systems for market making, you get:
- Faster response time for market making
- Scalability in market making
- 24x7 availability for market making
Faster response time for market making
Pricing of derivatives that enable investors to hedge often involves time-consuming mathematical calculations. While humans can take minutes, automated systems are so fast that they can do these calculations in microseconds. So they operate with much faster response time. Hence, stock market mathematics is an important concept to be learnt.

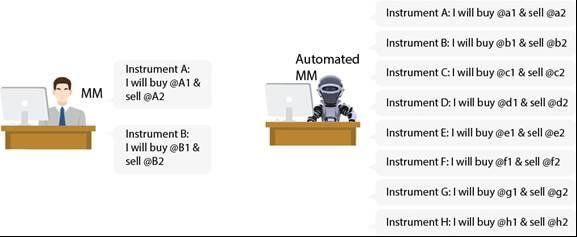
Scalability in market making
Speaking of scalability, while human traders can only track activities in a few instruments, automated systems can do the work in thousands of them simultaneously. Also, an automated trading system provides liquidity in significantly more financial instruments.
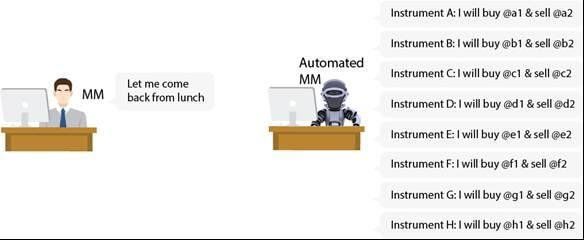
24x7 availability for market making
We are mentioning 24x7 availability in a literal sense here since machines do not take or need any breaks. As machines can go on working all the time and that too without any errors, they are much faster along with being accurate.
Difference between a broker and a market maker
It is a well-known fact that there are many market participants who play important roles in their own ways in financial markets.
However, market makers and brokers are two such participants who differ by various points, although both help the financial markets. Since they are often confused with Market Makers, we will see the points where they differ.
Brokers are the individuals who sell and buy stocks on behalf of the investors (clients). They are regulated and need registration with the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
To help your understanding of the difference between Brokers and Market Makers easier, we have put below the main points of differentiation:
|
Broker |
Market maker |
|
Brokers buy and sell stocks on behalf of investors. |
Market makers provide liquidity in the market by buying and selling stocks. |
|
Brokers provide their clients with profitable offers for buying or selling securities, stocks, mutual funds, etc. |
Market makers quote the stock prices based on the bid-ask spread in the markets. |
|
Brokers can be individuals or firms. |
Market makers are usually large banks or financial institutions. |
|
Brokers are intermediaries for their clients and financial markets. |
Market makers act like wholesalers in the financial markets by buying and selling securities. |
|
Brokers do not reflect market demand and supply as they do not set prices. |
Based on the prices they set, market makers reflect market demand and supply. |
|
They provide various services like consulting, research, investment advice and so on. |
Market Makers do not provide services to the clients and instead, they create the market for investors. |
How to become a market maker?
With the right knowledge and the application of the same, one can be successful at market making. Let us now see the different aspects for becoming a market maker.
Knowledge needed to become a market maker
For becoming a market maker, one needs to have a thorough knowledge and understanding of the financial markets and the experience with trading.
What to do to become a market maker?
Market makers become one by participating in the market and by earning through the spread between the bid and offer price of the securities. Because market makers bear the risk of covering a given security, which may drop in price, they are compensated for this risk of holding the assets.
For example, consider an investor who sees that Apple stock has a bid price of $50 and an ask price of $50.10. This implies that there exists an opportunity for a market maker to buy the Apple shares for $50 and sell them for $50.10. This way the market maker will earn a profit of $0.10.
Working of a market maker
A number of market makers operate and compete with each other within securities exchanges to attract the business of investors through setting the most competitive bid and ask offers.
In some cases, exchanges like the NYSE use a specialist system where a specialist is the sole market maker. This specialist makes all the bids and asks that are visible to the market. Also, a process is conducted to ensure that all marketable trades are executed at a fair price in a timely manner.
Awesome! With a thorough read of this article you must have got a fair understanding of market making.
Conclusion
We learnt all about market making strategy, market makers, as well as how and how much market makers earn.
With market making strategy, the market makers perform from both the sides i.e., by buying and selling in the markets. This way they not only create the market, but also earn profit by selling at a slightly higher price than the market price.
After that we found out the role of automation in making market makers stronger, the relevance of market making, and the difference between a broker and a market maker.
Great! We will call it a perfect start to your endeavour in market making.
If you wish to learn to identify trading opportunities based on Mean Reversion theory, and create different mean reversion strategies, the Mean Reversion Strategies In Python course by Quantra is a must for quant traders, offered by Dr. Ernest P Chan. Be sure to check it out.
Note: The original post has been revamped on 16th January 2023 for accuracy, and recentness.
Disclaimer: All investments and trading in the stock market involve risk. Any decision to place trades in the financial markets, including trading in stock or options or other financial instruments is a personal decision that should only be made after thorough research, including a personal risk and financial assessment and the engagement of professional assistance to the extent you believe necessary. The trading strategies or related information mentioned in this article is for informational purposes only.

