Cryptocurrency is digital money that uses advanced security techniques for safe transactions and is not controlled by any central authority as of now in India. Nevertheless, cryptocurrencies are regulated in some countries such as France, U.S.A, Canada, Australia, Germany, and Denmark to name a few.
The crypto market is gaining popularity, and many people are now trading it to potentially reap good returns. If you're curious about this exciting world of cryptocurrency trading, then this guide is for you!
To start trading, you'll need to get familiar with the crypto basics. For that matter, this guide covers the fundamentals of cryptocurrency and trading for beginners. But one must remember that knowledge is power, so keep learning and exploring!
This blog covers:
- What is a cryptocurrency?
- Examples of popular cryptocurrencies
- How does cryptocurrency work?
- Getting started with trading cryptocurrency
- Steps for buying and selling cryptocurrencies
- What are the different payment methods to trade crypto?
- Storing and securing cryptocurrencies
- Challenges with cryptocurrency and how to overcome them?
- Future of cryptocurrency
- How to learn crypto basics?
What is a cryptocurrency?
Imagine cryptocurrency as digital money that uses advanced security techniques and doesn't have a physical form like coins or bills. Instead, it has a virtual existence. You might have heard of Bitcoin, the first cryptocurrency, popular due to its stellar performance.
These digital currencies work on decentralised networks called blockchains. Think of a blockchain as a super-secure public ledger that records all transactions and can't be changed or controlled by anyone.
Cryptocurrencies don't need banks or governments to function. They operate independently, allowing people to send money directly to each other without any middlemen.
Examples of popular cryptocurrencies
Some major cryptocurrencies are Bitcoin, XRP, EOS, Ethereum, to name a few.

How does cryptocurrency work?
Let us find out different aspects of the working of cryptocurrency below.
Blockchain
A blockchain is a public and immutable ledger that records all transactions made with the cryptocurrency. It consists of a series of blocks, each containing a list of transactions. The blocks are linked together in chronological order, forming a chain of information.
Imagine digital money, but instead of banks and governments controlling it, there's a big online network that takes care of everything. This network is called a blockchain, and it's like a giant, super-secure digital ledger that keeps track of all the transactions made with that cryptocurrency.
This ledger isn't stored in one place - it's spread across a bunch of computers all over the world. Each of these computers has a copy of the entire blockchain, so it's decentralised and not controlled by any single entity.
Security
To keep everything safe and private, they use advanced cryptography. It's like writing in secret code, so only the people involved in a transaction can understand what's going on.
When you make a transaction, it's sent to this network, and all those computers work together to make sure it's legit. Once they agree, the transaction is recorded in a block, and that block is added to the chain of blocks - the blockchain.
Cryptocurrency mining
Now, some cryptocurrencies, like Bitcoin, use a process called "mining." Miners are like computer detectives - they solve complicated puzzles to verify transactions. The first one to solve the puzzle gets rewarded with some new coins.
Once a transaction is on the blockchain, it can't be changed or deleted - it's there forever. This makes everything transparent and trustworthy.
Decentralisation
Unlike traditional centralised financial systems, cryptocurrencies operate in a decentralised manner. This means that there is no central authority, such as a government or a bank, controlling the currency. Instead, the network is maintained by a distributed group of computers (nodes) that work together to validate and record transactions on the blockchain.
So, that's the basic idea of how cryptocurrency works - it's a clever mix of decentralisation, blockchain technology, and cryptography, making it a secure and transparent way to handle digital money without banks or middlemen!
Transactions
When someone wants to send cryptocurrency to another person or entity, they initiate a transaction. This transaction includes information about the sender, receiver, and the amount of cryptocurrency being transferred. Once the transaction is created, it is broadcast to the network.
Validation and Consensus
To ensure the security and integrity of the blockchain, transactions need to be validated. Different cryptocurrencies use different consensus mechanisms to achieve this. The most well-known is Proof-of-Work (PoW), used by Bitcoin, where miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. Other cryptocurrencies, like Ethereum, are moving towards Proof-of-Stake (PoS), where validators are chosen to validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold as collateral.
Block Addition
Validated transactions are grouped into a block. Once a block is completed, it is added to the blockchain. This process is continuous, and new blocks are added at regular intervals, forming a chronological chain of transactions.
Getting started with trading cryptocurrency
Here's a step-by-step guide to get you started!
Educate yourself about cryptocurrency and blockchain
Understand the basics of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. It's essential to grasp the concepts before diving in.
Define your objectives for getting involved
Decide why you want to get involved in cryptocurrency. Whether it's for investment, trading, or just curiosity, setting clear objectives will guide your actions.
Choose a reputable cryptocurrency exchange
Select a reliable cryptocurrency exchange to buy, sell, and trade digital assets. Look for a platform with a good reputation and strong security measures.
Complete the verification process
Most exchanges require verification to comply with regulations and ensure a secure trading environment. Follow the verification process to get started.
Set up a secure digital wallet
Get a digital wallet to store your cryptocurrencies safely. Choose from hardware wallets, software wallets, or mobile wallets, each with varying levels of security.
Implement strong security measures for your wallet
Safeguard your wallet with strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for an extra layer of protection.
Conduct thorough research on cryptocurrencies
Investigate different cryptocurrencies before making investment decisions. Understand their technology, use cases, and potential risks.
Develop a risk management strategy
In your risk management strategy, you must keep in mind how much you're willing to invest and set stop-loss orders to manage potential losses.
Start with small investments
Begin with a cautious approach by investing small amounts. This way, you can learn and minimise potential losses.
Stay updated with market news and trends
Keep an eye on cryptocurrency news, market trends, and developments to make informed decisions and adapt to the ever-changing landscape.
Steps for trading cryptocurrencies
Let us now see the steps related to buying and selling (trading) cryptocurrencies.

Step 1: Choose an Exchange
Research and select a reputable cryptocurrency exchange that supports the cryptocurrencies you want to buy.
Step 2: Create an Account
Sign up on the chosen exchange and complete the required verification process to comply with regulations.
Step 3: Fund Your Account
Deposit funds into your exchange account using fiat currency (e.g., USD, EUR) through bank transfers or other payment methods accepted by the exchange.
Step 4: Select a Cryptocurrency
Decide which cryptocurrency you want to buy or sell and check its current price on the exchange.
Step 5: Place a sell or buy order
Enter the amount of cryptocurrency you wish to buy or sell and review the details before confirming the order.
What are the different payment methods to trade crypto?
Here are a few options you can choose from:
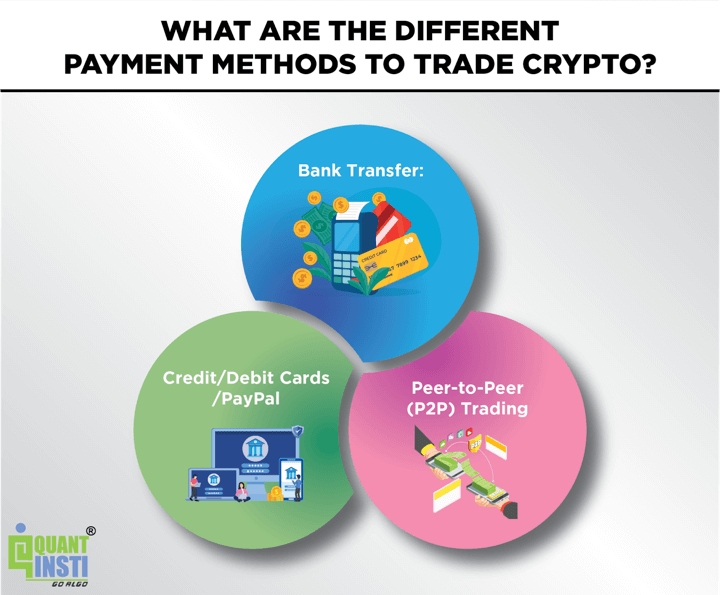
- Bank Transfer: Transfer funds directly from your bank account to the exchange. It's a common and secure method but may take longer for processing.
- Credit/Debit Cards/PayPal: Some exchanges allow buying cryptocurrencies with credit or debit cards and PayPal for instant purchases, but it might involve high fees per transaction. This can be anywhere over 3.75% plus additional fees based on the pairing.
- Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Trading: Certain platforms facilitate direct transactions between users.
Storing and securing cryptocurrencies
Storing and securing cryptocurrencies requires a thorough knowledge of the wallets and security measures to protect your digital assets effectively.
Let us take a look at:
- Types of wallets
- Backup and recovery options
- Importance of strong passwords and two-factor authentication
Types of wallets
Hot Wallets: Hot wallets are connected to the internet and accessible through various devices like smartphones, computers, or tablets. They provide convenient and quick access to your cryptocurrencies for daily transactions and trading. However, their online presence makes them more susceptible to hacking and security breaches.
One major drawback of hot wallets is that it is vulnerable to hacking and security breaches. Since hot wallets are connected to the internet, they are more susceptible to hacking attempts and online security breaches. If not adequately protected, hackers can gain unauthorised access to your private keys and steal your cryptocurrencies.
Cold Wallets: Cold wallets, also known as offline wallets, store your cryptocurrencies offline, away from the internet. They offer higher security since they are not vulnerable to online attacks. Cold wallets can come in various forms, such as hardware wallets (physical devices), paper wallets (printed private keys), or even offline software wallets that are not connected to the internet.
There are a few drawbacks of using cold wallets and these are:
- Inconvenience for Frequent Transactions: Cold wallets are primarily designed for long-term storage and security. If you need to make frequent transactions or quickly access your funds, the process of connecting your cold wallet to the internet each time can be cumbersome and less convenient compared to using a hot wallet.
- Risk of Physical Damage or Loss: Cold wallets, especially hardware wallets and paper wallets, are physical devices or documents that can be subject to damage, loss, or theft. If you lose your hardware wallet or misplace your paper wallet, there may be no way to recover the funds stored in them, leading to a permanent loss of your cryptocurrencies.
- Technical Complexity: Some types of cold wallets may require technical expertise to set up and use properly. For beginners or users who aren’t tech savvy, understanding the process of creating and managing a cold wallet can be challenging and might lead to mistakes that could compromise the security of their funds.
- Initial Cost: Cold wallets, especially hardware wallets, can have an upfront cost. While they offer excellent security features, this initial investment may be a deterrent for some users who prefer free or lower-cost alternatives.
Despite these drawbacks, cold wallets remain a popular choice for those seeking maximum security for their cryptocurrency holdings, especially for long-term storage and significant amounts of funds. Many cryptocurrency users opt for a combination of hot and cold wallets to balance convenience and security based on their specific needs and usage patterns.
Backup and recovery options
Backup: Backing up your cryptocurrency wallet is crucial to avoid losing access to your funds in case of device loss, damage, or other unforeseen circumstances. Most wallets provide an option to generate a recovery seed or mnemonic phrase—a series of words that act as a backup for your wallet's private keys. It's essential to securely store this backup in a separate physical location.
Recovery: If you encounter any issues with your wallet or need to set it up on a new device, you can use the recovery seed or mnemonic phrase to restore your wallet and regain access to your cryptocurrencies.
Importance of strong passwords and two-factor authentication
Strong Passwords: Creating a strong and unique password for your cryptocurrency wallet is vital to protect against unauthorised access. Avoid using easy passwords and opt for a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Long and complex passwords provide better security.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enabling two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security to your wallet. With 2FA, you'll need to provide a second form of verification, such as a unique code sent to your mobile device, in addition to your password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorised access, even if someone manages to obtain your password.
Challenges with cryptocurrency and how to overcome them?
|
Challenges with Cryptocurrencies |
Explanation |
Steps to overcome them |
|
Price Volatility |
Cryptocurrency prices can experience significant and rapid fluctuations, which can lead to potential losses or gains. |
Diversify investments across different cryptocurrencies and other assets. Set stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. |
|
Security Risks |
Cryptocurrencies are digital assets susceptible to hacking, phishing attacks, and other security breaches. |
Use reputable cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets. Implement strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA). Consider hardware wallets for added security. |
|
Regulatory Uncertainties |
Cryptocurrency regulations vary by country, and the legal framework is still evolving, leading to uncertainty for retail investors. |
Stay informed about the latest regulations in your country. Choose compliant exchanges and follow tax guidelines. |
|
Scams and Fraudulent Schemes |
The cryptocurrency space attracts scams and fraudulent schemes, such as fake ICOs or phishing scams. |
Be cautious of offers that seem too good to be true. Avoid sharing sensitive information or sending funds to unknown parties. |
|
Technical Issues and User Errors |
Technical glitches or user mistakes can lead to loss of access to funds or incorrect transactions. |
Double-check transaction details before confirming. Keep your wallet and software up-to-date. Backup your wallet securely. |
|
Market Manipulation and Speculation |
The cryptocurrency market can be influenced by market manipulation and speculative behaviour due to lack of regulation. |
Rely on reputable sources for information and avoid making decisions based on rumours or emotions. |
|
Lost or Forgotten Access Credentials |
Losing access to your wallet's recovery seed or private keys can lead to permanent loss of funds. |
Securely store your recovery seed or private keys in a separate physical location. Consider using password managers. |
Addressing these challenges can help individuals navigate the world of cryptocurrencies more confidently and safeguard their digital assets effectively. Always exercise caution, conduct thorough research, and stay updated with the latest developments in the crypto space.
Future of cryptocurrency
In the future, regulatory challenges related to crypto may persist as governments grapple with how to approach this rapidly evolving space. Cryptocurrency markets may continue to be volatile, requiring investors to exercise caution and make informed decisions.
However, The future of cryptocurrency also holds the potential for significant advancements. We might witness cryptocurrencies becoming more mainstream, integrated into everyday transactions, and accepted globally. Security measures are likely to improve, providing users with better protection against hacking and fraud.
Blockchain technology, the backbone of cryptocurrencies, is expected to revolutionise various industries beyond finance. We might see its integration in supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems, bringing greater transparency and efficiency.
To navigate the future of cryptocurrency successfully, stay informed about the latest developments, conduct thorough research before investing, and remember that this market is still maturing. As with any investment, only risk what you can afford to lose, and keep a long-term perspective.
Embrace the opportunities while being mindful of the risks, and enjoy the exciting journey ahead!
Disclaimer: We do not endorse or encourage the trading of any financial instrument in any market. Engaging in trading activities is solely at the discretion and responsibility of the individual trader. It is essential for traders to conduct their own research, assess risks, and make informed decisions. The information provided should not be considered as financial advice.
How to learn more about cryptocurrency?
After going through the crypto basics, you must learn more about crypto trading strategies through some popular sources such as online courses and blogs.
Courses
There are two courses we can recommend for those who are interested in taking the next step after learning crypto basics.
- Crypto Trading Course: Intermediate First of all, you can learn from the intermediate course so as to gain more insights into the world of cryptocurrency after learning the basics.
- Crypto Trading Strategies: Advanced: Secondly, you can move to the advanced course to learn using advanced ways of trading cryptocurrencies such as using machine learning and statistical arbitrage for the same.
Blogs
Further, you can learn more about cryptocurrencies through blogs as mentioned below.
- Cryptocurrencies Trading Strategy With Data Extraction Technique
- Basics Of Forex Trading For Beginners
- Aroon Indicator: How To Use It For Cryptocurrency Trading
- Top 9 Cryptocurrency Trading Platforms
Bibliography
- https://www.coinbase.com/learn/crypto-basics
- https://www.oswego.edu/cts/basics-about-cryptocurrency
- https://www.moneycontrol.com/msite/wazirx-cryptocontrol-articles/a-beginners-guide-to-cryptocurrency-article/
Conclusion
Cryptocurrency is a thrilling world with opportunities and challenges. Understand what it is and how it works before trading. Educate yourself before you delve into trading. Stay updated with market trends and develop risk management strategies.
Remember, it's a dynamic space with potential for growth, but be cautious and learn the basics to make the most of it!
If you wish to learn more about cryptocurrencies, enrol into the course on Crypto Trading Strategies: Intermediate.
Disclaimer: All data and information provided in this article are for informational purposes only. QuantInsti® makes no representations as to accuracy, completeness, currentness, suitability, or validity of any information in this article and will not be liable for any errors, omissions, or delays in this information or any losses, injuries, or damages arising from its display or use. All information is provided on an as-is basis.


