Cloud computing is an integral part of most businesses. Because of the convenience, security and reliable services that it provides, cloud computing is finding widespread applications in the world of trading. Especially since a user can work from anywhere and everywhere.
In today’s contemporary world where it is raining data everywhere, cloud computing is proving to be a boon for retail traders, institutions and almost everyone who is a part of the financial markets.
This article covers:
- What is cloud computing?
- History of cloud computing
- Types of cloud services
- Types of cloud computing deployment models
- Example of cloud-based trading platform
- How can cloud computing be used in automated trading systems?
- Cloud computing in retail trading
- Cloud computing in the Forex market
- Prerequisites for using cloud computing service in trading
- Benefits of using cloud computing in trading
- Challenges of using cloud computing in trading
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the Internet (“the cloud”).
Cloud computing is a service that is designed to be accessible to anyone and everyone using the internet. It is an open platform that one needs to land on via internet connectivity without needing any hardware or software for the same.
Different companies and industries of all types, sizes and business types are using the cloud for a wide variety of reasons, such as data backup, disaster recovery, virtual desktops requirements, software development, big data analytics, etc.
For example, hospitals are using the cloud to develop more personalised treatments for patients. Similarly, financial services companies are using the cloud to power real-time fraud detection and prevention.
Also, it is expected that the cloud computing market size will soon be valued at US$ 405,295.8 million in 2022 and reach US$ 1,465,818.2 million by 2028.
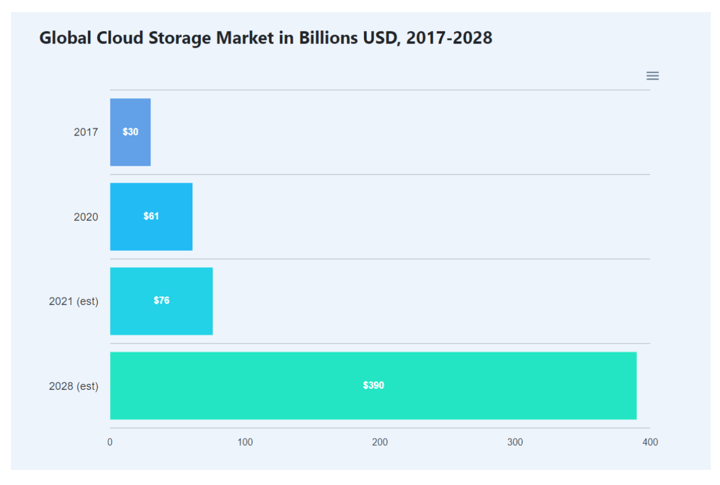
Since cloud computing offers faster innovation and flexible resources, it is quite convenient. Moreover, a cloud computing platform like Blueshift is free of cost which also helps you be sure of low costs. Start automating your trades with a top Algorithmic Trading Platform.
As time progresses, cloud computing in finance is rapidly gaining widespread appeal.
History of cloud computing
The history and evolution of cloud computing date back to the 1950s and 1960s. In the 1950s, companies started to use large mainframe computers. But since it was too expensive to buy a computer for each user, during the late 1950s and early 1960s, a process called time sharing was developed.
The time sharing implied the facility to connect multiple computers to the mainframe. The mainframe consisted of more memory and increased processing power as compared to the other computers.
Hence, connecting the mainframe with other computers led to the sharing of the mainframe’s memory and processing power with those connected computers.
The time sharing helped to make more efficient use of expensive processor time on the mainframe computer by connecting the same with other multiple computers.
In the 1970s, cloud computing began taking a more tangible shape with the introduction of the first virtual machine, enabling users to run more than one computing system within a single physical setup.
The functionality of these virtual machines led to the concept of virtualization, which had a major influence on the progress of cloud computing.
In a 2021 survey by Google, it was found that:
- 93% of exchanges, trading systems and data providers offer cloud-based data and services.
- 67% of commercial and investment banks consume cloud-deployed market data.
- 90% of surveyed buy-side firms consume cloud-deployed market data, mostly for portfolio management.
In their article, Cybersecurity ventures predict that the global data storage on the cloud will expand to 100 zettabytes by 2025 - a zettabyte is a billion terabytes (or a trillion gigabytes).
Types of cloud services
Cloud computing service is available in three different models namely Saas, PaaS and IaaS. Although all three are often portrayed as stacked layers, each provider can even offer any one of them.
For example, a provider can offer SaaS implementation for trading features, without using underlying PaaS or IaaS layers. Similarly, one can run a program on IaaS and access it directly, without the need for SaaS.
Let us learn more about each model further.

Software as a service (SaaS)
Users gain access to application software and databases in the software as a service (SaaS) model. Cloud providers manage the infrastructure and platforms that run the applications. In the SaaS model, cloud providers install and operate application software in the cloud and cloud users access the software via the provider.
Platform as a service (PaaS)
In PaaS, cloud providers deliver a platform, typically including an operating system, programming-language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers develop and run their software on a cloud platform instead of directly buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a service or IaaS refers to online services that provide high-level APIs used to abstract various low-level details of underlying network infrastructure like physical computing resources, location, data partitioning, scaling, security, backup, etc.
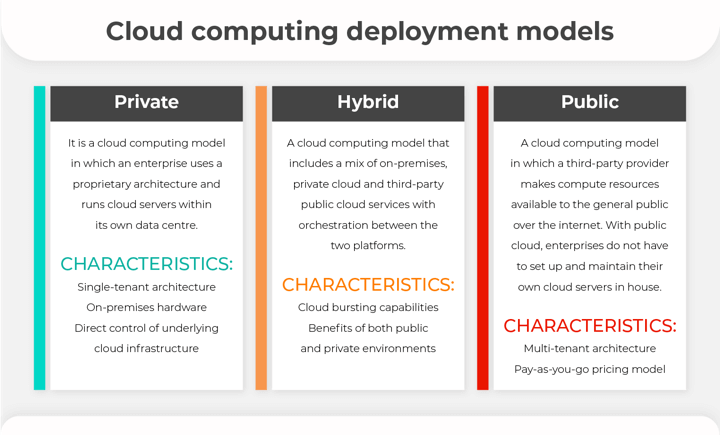
Types of cloud computing deployment models
The cloud computing models are of three types. Let us see what are those three types briefly:
Private Cloud
Private cloud is a cloud computing model in which an enterprise uses a proprietary architecture and runs cloud servers within its own data centre.
Hybrid Cloud
The hybrid cloud is a cloud computing model that includes a mix of on-premises, private cloud and third-party public cloud services with orchestration between the two platforms.
Public Cloud
Public cloud is a cloud computing model in which a third-party provider makes computing resources available to the general public over the internet. With the public cloud, enterprises do not have to set up and maintain their own cloud servers in-house.
Example of cloud-based trading platform
A cloud-based trading environment offers flexibility and business continuity by allowing traders to work from simply anywhere possible. Cloud-based trading platforms offer connectivity through cloud platforms, increasing efficiency and cutting costs.
Let us see an example of cloud based trading platform, that is, Blueshift.
Blueshift is a FREE platform to bring institutional class infrastructure for investment research, backtesting and algorithmic trading to everyone; anywhere and anytime. Also, there is a newly launched alpha version - a fast backtesting platform with minute-level data covering multiple asset classes and markets.
On Blueshift, you have to explicitly choose a dataset while running a strategy for backtesting. You must pick a dataset consistent with your strategy.
For example, if you developed a strategy to trade Apple, you must choose the NYSE datasets to run it without error. At present, we have the following datasets available for research/ backtests):
- Equities and ETFs market data for the US market and India – minute levels with corporate actions. Updated once every day after market close.
- Futures data for NSE (India) monthly futures (first three contracts) – minute levels with adjustments. Updated once every day after market close.
- FX data - 10 currency pairs - AUD/USD, EUR/CHF, EUR/JPY, EUR/USD, GBP/JPY, GBP/USD, NZD/USD, USD/CAD, USD/CHF, USD/JPY. Minute-level data is updated once every day.
- Crypto data - 9 coins against Tether (USDT) and Indian Rupees (INR), also includes USDT/INR. The nine coins are BTC, ETH, ADA, BNB, MATIC, XRP, SOL, DOT and LUNA. You must specify them as pairs, either against USDT (e.g. BTC/USDT) or INR (e.g. BTC/INR).
You can research your ideas, backtest them, and take your strategies live with a broker of your choice on Blueshift.
Brokers available on Blueshift are Alpaca, FXCM and MASTERTRUST for live trading. For paper trading, the brokers available are Alpaca and FXCM.
How can cloud computing be used in automated trading systems?
For using cloud computing in trading, one needs to follow the steps required for using the cloud service.
For instance, Blueshift requires the following steps for using the cloud service in trading.
- Step 1 - Sign up!
You simply need to register and sign up for creating an account. - Step 2 - Create a strategy
You will get the strategy template to create the strategy you want. For instance, you can create an options strategy with put and call options. Also, you will give a name to that strategy. - Step 3 - Write and optimise strategy
Next, you will write and optimise the strategy. You will be taken to the page where you can write your algorithm. Also, you can optimise the returns and other metrics on the same page. - Step 4 - Backtest
Now, you can enter the dataset you would like to use for the backtest, the beginning date, the ending date, and the capital amount for the algorithm. To run the quick backtest, select run. - Step 5 - Go live!
Finally, you go live with your strategy by clicking the “go live” button.
Cloud computing in retail trading
The concept of cloud computing is an on-demand self-service Internet infrastructure where you ‘pay-as-you-go’ and use what you need. Retail traders are slowly venturing into this form of digital technology to execute their trading strategies based on the convenience of the cloud.
Due to the convenience of the cloud, traders can use the cloud service to create new trading strategies, backtest on historical data and run time series analysis along with executing trades.
With cloud computing, instead of building the data centre infrastructure themselves, they can test the strategy as long as they need to and if it doesn’t work out, they can shut it down and terminate the payment for the same.
This concept of renting space and time over the cloud is far more viable than creating one’s own hardware/software infrastructure.
This same concept runs in trading related software – Software as a Service (SaaS) that a trader can use and run on demand. Analytics, research and testing of trading strategies are reasons why retail trading is migrating to the cloud.
In conclusion, the cloud is not an industry or a category, it is an ecosystem. Retail traders are switching to cloud computing because it helps cut costs, maximise resources and increase efficiencies thus resulting in phenomenal outputs in their trading strategies.
Cloud computing in the Forex market
The Forex market is an Over the Counter (OTC) market for trading currencies. This market is open 24 hrs and 5.5 days a week where currencies are traded via computer networks between traders around the world.
In a global market that never sleeps, how are Forex traders leveraging cloud services? Forex traders with automated trading systems are putting them on a broker’s cloud or with an independent Virtual Private Server (VPS) company.
Prerequisites for using cloud computing service in trading
To use cloud computing services in Trading, the following skills would be required.
Programming
A programming language (Python, R, MATLAB) is a prerequisite for any new aged trader who wants to make use of technological and computational advancements such as backtesting on historical data.
Backtesting
Since cloud computing service offers backtesting as one of the features, one must have the knowledge of backtesting the strategies. Backtesting is the process of testing a trading strategy using historical data to determine the effectiveness of that strategy.
Backtest results usually show the strategy’s performance in terms of popular performance metrics like the Sharpe ratio and Sortino ratio. The performance metrics usually help to quantify the return over risk.
Knowledge of parameters
For using the cloud computing service, a trader must have a sound knowledge of the parameters to utilise such as stop orders for limiting losses. This way, the cloud service can be used in the best possible manner.
Knowledge of platform
It is also important to know how the cloud platform that you are working with works. This requires the user to go through all the necessary information about the working of the platform in a section that explains it all.
For instance, the Blueshift documentation helps you find everything you need to know about the platform.
Further, as a user of the cloud platform, it is important to note that there are other areas of which you should be aware, such as:
- The regulations surrounding the use of cloud service
- Networking
- Database
- Virtualisation
- Operating system
These are a few points out of many that the cloud provider takes care of, but you need to be aware of them as the user.
Benefits of using cloud computing in trading
Now let us discuss the benefits of using cloud computing in trading for the users. The benefits are as follows-
Reliability
Cloud computing in trading offers reliability since the data you input is stored across multiple servers and your provider might even have the feature of storing it in multiple locations. Hence, the data stored is safer than storing it on your hard drive since hard drive data may be lost due to reasons such as formatting, system failure owing to technical faults etc.
Cost reduction
Some cloud computing platforms are free (like Blueshift) and others (like Cloud9) come at a lower cost. This cost is compared to the expenditure on hardware, software, maintenance of the hardware and software etc.
Flexibility and mobility
Cloud computing offers flexibility and mobility to the user since the cloud service merely needs a system with an internet connection. One can access the cloud platform from anywhere and everywhere. Hence, there is no need to keep your system with the concerned software handy at all times.
Challenges of using cloud computing in trading
The challenges of using cloud computing in trading are not less but manageable. Let us see what all you need to know about the downsides of using cloud computing for trading:
Downtime
This is one of the disadvantages when it comes to your internet being down. In case of downtime with your internet, there is nothing that can be done on the cloud.
Security issues
Since cloud computing service is available and accessible to everyone, security is an issue. To ensure security, you must follow the basic security measures such as encryption, not sharing your password with anyone and having a backup of your data (just in case!)
Lack of expertise
For using the cloud computing service, it is essential to have expertise so that you can easily navigate through the features of the platform and utilise the same. For building the expertise, it is important to read through the documentation of the platform.
Also, it is important to be knowledgeable with regard to necessary areas such as programming, knowledge of markets, performance metrics, strategy creation etc. When the expertise is not up to the mark, it can lead to performance issues.
Compliance
The user of the cloud platform needs to follow the rules and regulations set by the platform. When the user does not abide by the rules or compliance, it is a problem.
Building a private cloud and managing multiple clouds
This is a wide topic as it is but there are a lot of challenges around building a private cloud as well as managing multiple clouds.
Building a private cloud requires a lot of prerequisites such as needing to set up computation, network and storage resources, installing management software for the hardware etc. Similarly, in the case of managing multiple clouds, the security issues include misconfiguration of security and privacy settings etc.
The challenges could vary depending on your knowledge and expertise in the domain, the resources available to you, regulations, charges, and more.
The following graph from Cloudwards shows the most common and pressing cloud security concerns and the percentage of occurrence of each.

Conclusion
Cloud computing is used across the globe to make the work of professionals easier and more efficient with advantages such as a reliable set up and reduced costs. By managing the challenges related to cloud computing, one can successfully trade, backtest and find the right strategies for implementation in different situations in the market.
Although it has its fair share of benefits and challenges in trading, cloud computing is evolving, improving and racing towards becoming the next big thing in the world of technology and finance.
To learn more about quantitative trading for which the cloud services are used, you can explore this algo trading course which gives you a deep insight into the world of algorithmic trading. It teaches you everything that you would need to know about algo trading and also utilising it on a cloud platform.
Note: The original post has been revamped on 12th August 2022 for accuracy, and recentness.
Disclaimer: All investments and trading in the stock market involve risk. Any decision to place trades in the financial markets, including trading in stock or options or other financial instruments is a personal decision that should only be made after thorough research, including a personal risk and financial assessment and the engagement of professional assistance to the extent you believe necessary. The trading strategies or related information mentioned in this article is for informational purposes only.


